The Magnetron in Microwave Ovens: How It Works and Why It Matters
Microwave ovens are everyday appliances, yet few people realize the complex science behind how they work. At the heart of this innovation is the magnetron—a powerful device that turns electricity into microwave energy, allowing us to cook food in mere minutes. But what is a magnetron, how does it work, and why is it so essential to your microwave oven?
Let’s explore the inner workings of the magnetron, its importance, pros and cons, and what the future holds for this core microwave component.
1. 📡 What Is a Magnetron?
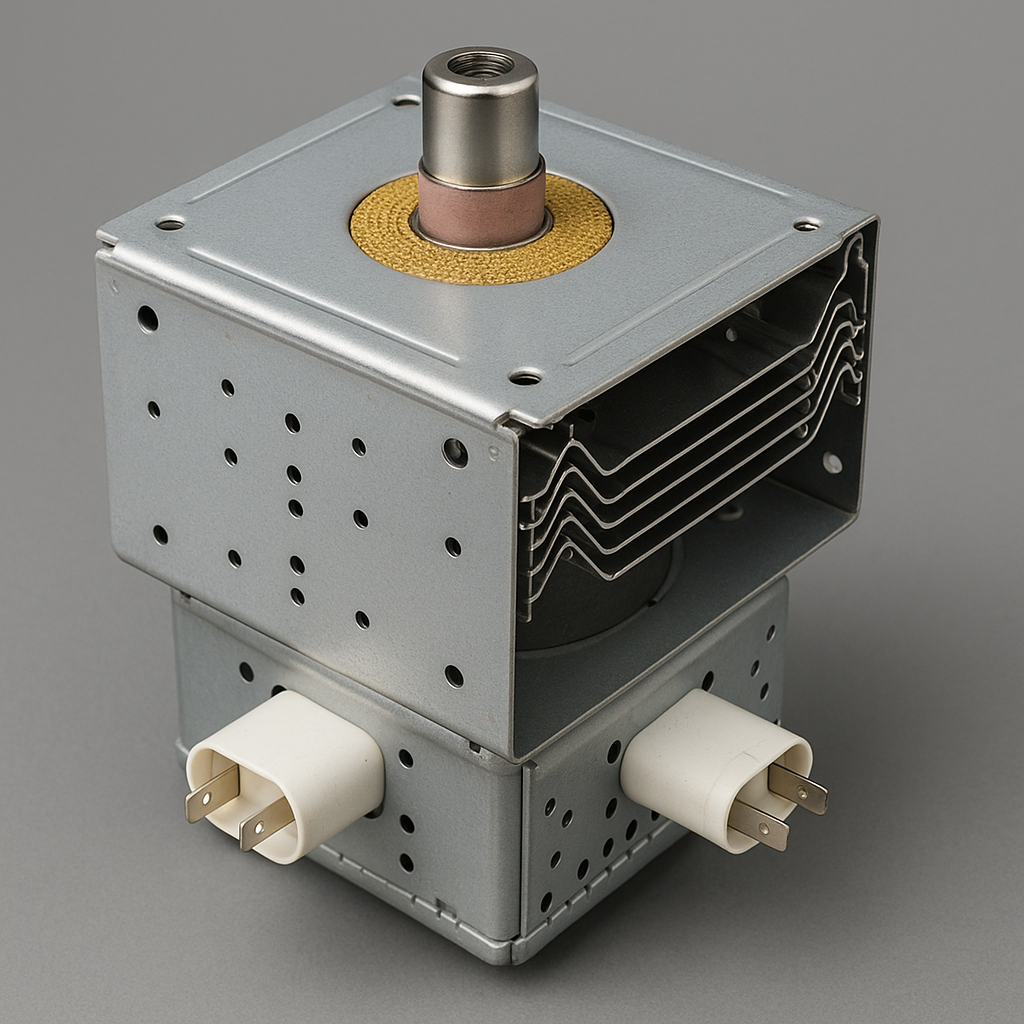
A magnetron is a high-powered vacuum tube used to generate microwave-frequency electromagnetic waves. These microwaves oscillate typically at 2.45 GHz (gigahertz), a frequency that’s highly effective for exciting water molecules—thus heating food efficiently.
🧪 A Glimpse into History
The magnetron was developed in the late 1930s and became famous during World War II for use in radar systems. British engineers John Randall and Harry Boot were instrumental in creating the cavity magnetron, which drastically improved radar performance. After the war, scientists realized this same technology could heat food—accidentally discovered when a radar technician’s chocolate bar melted in his pocket!
By the 1960s, companies like Raytheon and Amana adapted magnetron-based cooking into consumer microwave ovens, forever changing kitchen technology.
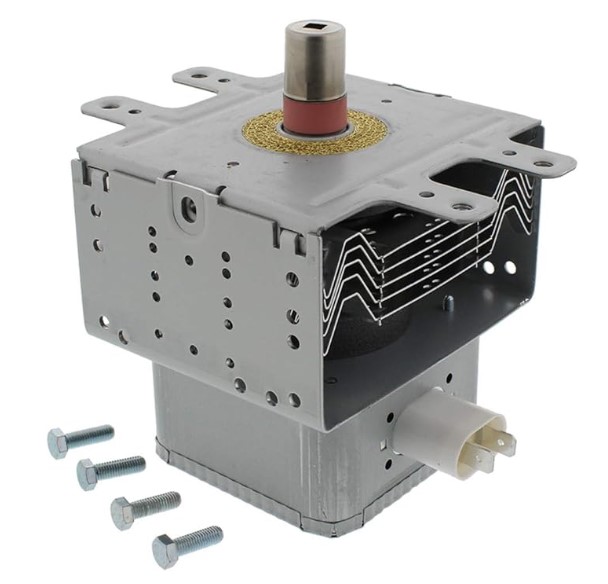

2. ⚙️ How Does a Magnetron Actually Work?
A magnetron transforms electrical energy into microwave radiation. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown:
🔧 Inside the Magnetron:
- Cathode (Heated Filament): Emits electrons when heated.
- Anode Block with Resonant Cavities: Metal block surrounding the cathode, containing cavities that determine the microwave frequency.
- Magnetic Field: Applied using permanent magnets, it curves the path of electrons.
- Spokes and Straps: These direct the electrons past cavities, creating oscillations.
- Antenna & Waveguide: Extracts and channels the microwaves into the cooking chamber.
As electrons spiral through the magnetic field, they pass the cavity resonators, generating powerful bursts of microwave energy, which is then funneled through the waveguide and distributed into the oven’s interior.
3. 🔩 Key Microwave Components That Support the Magnetron
Understanding how the magnetron fits into the larger system helps clarify its function. Here are other vital components it relies on:
⚡ High-Voltage Transformer or Inverter:
- Converts household AC power (110–240V) to 3,000+ volts needed to power the magnetron.
- Newer models may use inverter circuits for consistent power delivery.
📡 Waveguide:
- A metal tunnel that directs microwaves from the magnetron to the cooking chamber.
- Ensures efficient transfer of energy with minimal loss.
❄️ Cooling Fan and Airflow Vents:
- Prevents the magnetron from overheating by continuously circulating air.
- Some high-end microwaves have temperature sensors that adjust fan speed automatically.
🧠 Control Board:
- Sends signals to the transformer or inverter to turn the magnetron on or off.
- Controls timing, defrost cycles, and power levels.
4. 🔥 Common Magnetron Failures and Symptoms
Like any electronic component, magnetrons wear out. Here’s what to watch for:
| Symptom | Possible Cause |
|---|---|
| No heating | Failed magnetron or transformer |
| Humming or buzzing noise | Faulty internal components |
| Sparks inside the microwave | Waveguide damage or magnetron arcing |
| Burning smell or overheating | Magnetron degradation |
| Microwave trips circuit | Magnetron short or power surge |
🛠️ Tip: Magnetrons are dangerous to test or replace yourself due to high-voltage capacitors. Always contact a licensed appliance repair technician.
5. 🚀 Innovations & Alternatives to Traditional Magnetrons
While magnetrons still dominate most home microwaves, newer technologies are pushing boundaries:
Inverter Technology
- Provides variable power levels instead of simple ON/OFF cycles.
- Results in more even heating, perfect for delicate foods like chocolate or fish.
- More energy-efficient and extends the lifespan of internal components.
Solid-State RF Heating
- Uses semiconductor-based amplifiers (transistors) instead of vacuum tubes.
- Allows precise frequency control, multi-zone cooking, and smart sensors.
- Found in high-end or commercial appliances; more expensive but longer-lasting.
Dielectric Heating (Future Prospect)
- An emerging concept using dielectric fields rather than magnetrons.
- Allows even deeper penetration and avoids “hot spots.”
6. ⚠️ Safety Considerations: Why You Should Never DIY a Magnetron Repair
Magnetrons are not user-serviceable for good reason:
- High Voltage Danger: The microwave’s capacitor can store thousands of volts even after unplugging.
- Toxic Materials: Some older magnetrons contain beryllium oxide, a highly toxic ceramic insulator.
- Radiation Risk: Although microwaves are non-ionizing and contained by design, a damaged magnetron or door seal can leak energy.
🗑️ Safe Disposal
Always dispose of old microwaves or magnetrons at certified e-waste recycling centers. Never toss them in general trash.
Pros and ❌ Cons of Magnetrons
✅ Pros
- Fast and Efficient: Heats food in a fraction of the time conventional ovens take.
- Compact and Lightweight: Makes microwaves small enough for countertop use.
- Economical: Cheap to produce and widely available.
- Proven Reliability: Decades of use with consistent performance.
❌ Cons
- Shorter Lifespan: Typically lasts 5–10 years or 2,000–8,000 hours of use.
- Fixed Frequency: Leads to cold spots or uneven heating.
- Not Eco-Friendly: Contains hazardous materials and can be hard to recycle.
- High Voltage Hazard: Not safe for untrained users to handle.
❓ Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
A: The microwave may run but not heat. You may hear humming or see sparking. Internal damage can also trip electrical circuits.
A: Generally, no. Replacing the magnetron is safer, faster, and often more cost-effective.
A: Only if the microwave is damaged. Modern microwaves are built with shielding to prevent leakage.
A: Fixed-frequency magnetrons can cause hot and cold spots. Try using a turntable or microwave-safe stirrers.
A: Not traditional ones. Only solid-state or inverter systems can cook without using a classic magnetron tube.
🧠 Final Thoughts
The magnetron is the unsung hero of modern kitchen technology. It made fast, convenient cooking accessible to millions and remains central to most microwave ovens today. While newer technologies may eventually replace it, the magnetron’s contribution to the world of cooking is nothing short of revolutionary.
Knowing how it works, how to recognize failure signs, and why safety matters helps users make smarter choices—whether you’re troubleshooting issues or considering an upgrade to a newer model.





















Leave a Reply